 Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I
Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I
1. Name of Database: Plasma Particle Simulation I :
Computer Simulations of Electrostatic Solitary Waves in the Magnetotail
2. Institution:﹛ Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University
3. Contents of Database: ﹛
We present particle simulations of one of the most fundamental instabilities in plasmas,
i.e., two-stream instability induced by two groups of electrons moving with different drift
velocities. Electrostatic waves grow from the thermal fluctuation noise with the growth rate
predicted by the linear theory, and saturate due to nonlinear trapping of electrons by the
coherent electrostatic potentials. After the saturation, the series of the large amplitude
potentials coalesce with each other to form isolated potentials. This process was also
observed in the past Vlasov code simulations and laboratory experiments and were called as
electron holes. The plasma wave observation by the GEOTAIL spacecraft revealed that there
also exist electrostatic solitary waves similar to electrons holes in the plasma sheet
boundary layer of the Earth﹊s magnetotail. We performed electrostatic particle simulations
for various parameters and found conditions for generation of the ESW. The ESW is generated
as a results of nonlinear coalescence of strong electrostatic waves excited by an electrostatic
beam instability involving the electron beam drifting relative to the majority of ions and
another electrons drifting with the ions. We performed two runs with different initial ion
thermal velocities Vi. One is with Vi = 2.0, and the other is with Vi = 0.1. We assumed the
same density ratio R = 0.5 for these runs. Namely, two electron beams have the same thermal
velocity with drift velocities Vd and 0. The evolution of the instability is shown by the
phase diagrams of particle in the (X, Vx) space at different times. As a necessary condition
for formation of the ESW, the ion thermal velocity Vi must be large enough so that the
electrostatic waves due to the beam instability cannot decay to ion acoustic waves.
All computations were performed on the KDK computer system at Research Institute for Sustainable
Humanosphere, Kyoto University.
4. Examples of Database:
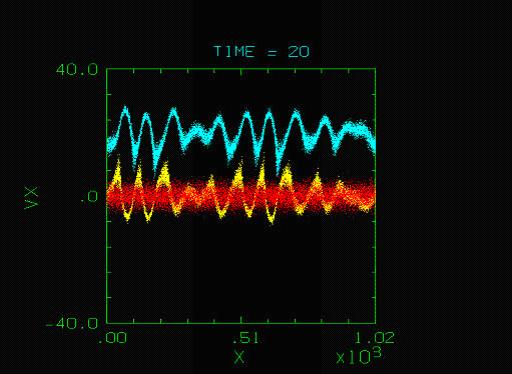
The database includes several kinds of plots showing detailed processes of nonlinear evolution
of electron two-stream instability. Among them phase space plots showing the locations of
electrons in the (X, Vx) phase space are most interesting. An example of the phase space plots
is shown below. The dots with red, yellow and cyan colors represent ions, electrons moving
with ions and electrons moving with a drift velocity Vd =20Ve , respectively. Both groups of
electrons have the same thermal velocity Ve. A reduced mass ratio of ions to electrons is
assumed to be 100. The time indicated on top of each figure is normalized by the inverse of
the total electron plasma angular frequency. Namely, ﹍TIME= 6.28﹎ corresponds to one period
of the total electron plasma oscillation.
 Detailed description of the simulation runs are found in the following reference.
Y. Omura, H. Kojima and H. Matsumoto, Computer Simulation of Electrostatic Solitary Waves:
A Nonlinear Model of Broadband Electrostatic Noise, Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 21,
pages 2,923-2,926, 1994.
The simulation code used in producing the present database. is a one-dimensional elelctrostatic coode.
Detailed description of the code is found in the following reference.
Y. Omura and H. Matsumoto, KEMPO1: Technical Guide to One-Dimensional Electromagnetic Particle Code,
Computer Space Plasma Physics: Simulation Techniques and Softwares, edited by H. Matsumoto and
Y. Omura, pages 21-65, Terra Scientific, Tokyo, 1993.
http://www.terrapub.co.jp/e-library/cspp/index.html
5. Contact:
﹛Yoshiharu Omura
﹛RISH, Kyoto University,
﹛Gokasho, Uji, 611-0011, Japan
﹛Phone: +81-774-38-3811
﹛E-mail: omura[AT]rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
6. Public Offering of Database:
﹛http://center.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/web1/sramp/cdrom/sm0004/index.html
﹛Also see:
﹛Home Page of Geotail Plasma Wave Instrument
﹛http://www.rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp/space/gtlpwi/
Detailed description of the simulation runs are found in the following reference.
Y. Omura, H. Kojima and H. Matsumoto, Computer Simulation of Electrostatic Solitary Waves:
A Nonlinear Model of Broadband Electrostatic Noise, Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 21,
pages 2,923-2,926, 1994.
The simulation code used in producing the present database. is a one-dimensional elelctrostatic coode.
Detailed description of the code is found in the following reference.
Y. Omura and H. Matsumoto, KEMPO1: Technical Guide to One-Dimensional Electromagnetic Particle Code,
Computer Space Plasma Physics: Simulation Techniques and Softwares, edited by H. Matsumoto and
Y. Omura, pages 21-65, Terra Scientific, Tokyo, 1993.
http://www.terrapub.co.jp/e-library/cspp/index.html
5. Contact:
﹛Yoshiharu Omura
﹛RISH, Kyoto University,
﹛Gokasho, Uji, 611-0011, Japan
﹛Phone: +81-774-38-3811
﹛E-mail: omura[AT]rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
6. Public Offering of Database:
﹛http://center.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/web1/sramp/cdrom/sm0004/index.html
﹛Also see:
﹛Home Page of Geotail Plasma Wave Instrument
﹛http://www.rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp/space/gtlpwi/
 CAWSES SPACE-W Databese List.
CAWSES SPACE-W Databese List.
CAWSES SPACE-W Home Page.
 Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I
Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I
Particle Simulation of Plasma Wave Instabilities I Detailed description of the simulation runs are found in the following reference.
Y. Omura, H. Kojima and H. Matsumoto, Computer Simulation of Electrostatic Solitary Waves:
A Nonlinear Model of Broadband Electrostatic Noise, Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 21,
pages 2,923-2,926, 1994.
The simulation code used in producing the present database. is a one-dimensional elelctrostatic coode.
Detailed description of the code is found in the following reference.
Y. Omura and H. Matsumoto, KEMPO1: Technical Guide to One-Dimensional Electromagnetic Particle Code,
Computer Space Plasma Physics: Simulation Techniques and Softwares, edited by H. Matsumoto and
Y. Omura, pages 21-65, Terra Scientific, Tokyo, 1993.
http://www.terrapub.co.jp/e-library/cspp/index.html
5. Contact:
﹛Yoshiharu Omura
﹛RISH, Kyoto University,
﹛Gokasho, Uji, 611-0011, Japan
﹛Phone: +81-774-38-3811
﹛E-mail: omura[AT]rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
6. Public Offering of Database:
﹛http://center.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/web1/sramp/cdrom/sm0004/index.html
﹛Also see:
﹛Home Page of Geotail Plasma Wave Instrument
﹛http://www.rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp/space/gtlpwi/
Detailed description of the simulation runs are found in the following reference.
Y. Omura, H. Kojima and H. Matsumoto, Computer Simulation of Electrostatic Solitary Waves:
A Nonlinear Model of Broadband Electrostatic Noise, Geophysical Research Letters, vol. 21,
pages 2,923-2,926, 1994.
The simulation code used in producing the present database. is a one-dimensional elelctrostatic coode.
Detailed description of the code is found in the following reference.
Y. Omura and H. Matsumoto, KEMPO1: Technical Guide to One-Dimensional Electromagnetic Particle Code,
Computer Space Plasma Physics: Simulation Techniques and Softwares, edited by H. Matsumoto and
Y. Omura, pages 21-65, Terra Scientific, Tokyo, 1993.
http://www.terrapub.co.jp/e-library/cspp/index.html
5. Contact:
﹛Yoshiharu Omura
﹛RISH, Kyoto University,
﹛Gokasho, Uji, 611-0011, Japan
﹛Phone: +81-774-38-3811
﹛E-mail: omura[AT]rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
6. Public Offering of Database:
﹛http://center.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/web1/sramp/cdrom/sm0004/index.html
﹛Also see:
﹛Home Page of Geotail Plasma Wave Instrument
﹛http://www.rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp/space/gtlpwi/